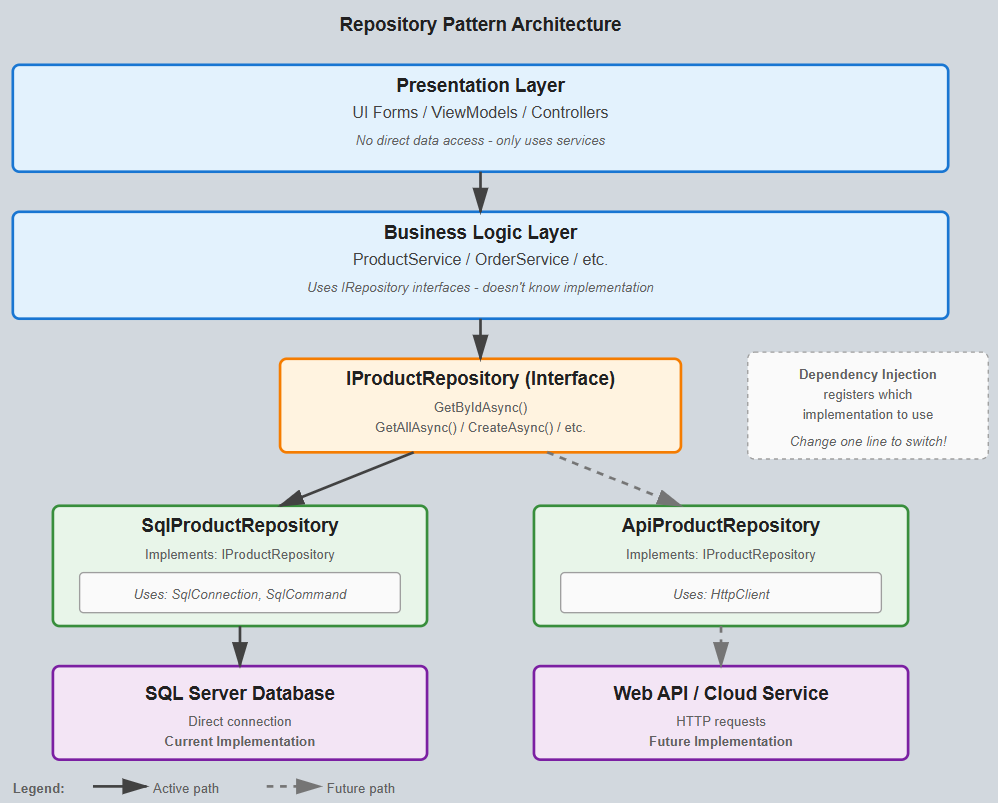
The best approach is to use the Repository Pattern with Dependency Injection. This creates a clean separation between your business logic and data access, making it straightforward to swap SQL Server for an API later.
Core Architecture
1. Define Interfaces (Contracts) Create interfaces that define data operations without specifying how they happen:
public interface IProductRepository
{
Task<Product> GetByIdAsync(int id);
Task<List<Product>> GetAllAsync();
Task<int> CreateAsync(Product product);
Task UpdateAsync(Product product);
Task DeleteAsync(int id);
}public class SqlProductRepository : IProductRepository
{
private readonly string _connectionString;
public SqlProductRepository(string connectionString)
{
_connectionString = connectionString;
}
public async Task<Product> GetByIdAsync(int id)
{
using var connection = new SqlConnection(_connectionString);
// Your SQL logic here
}
// ... other methods
}2. SQL Server Implementation Implement the interface for direct SQL Server access:
























